Day 4 : Variables, Data Types & User Input
Today I learned about variables, data types, and how to take input from the user.
This is an important foundation because almost every Python program stores and processes information.
What I Learned Today
- Variables are used to store values
- Python has multiple data types:
- str - text
- int - whole numbers
- float - decimal numbers
- bool - True/False
input()is used to collect user input- Input is always a string unless converted
int()orfloat()convert numbers- Functions can return calculated values
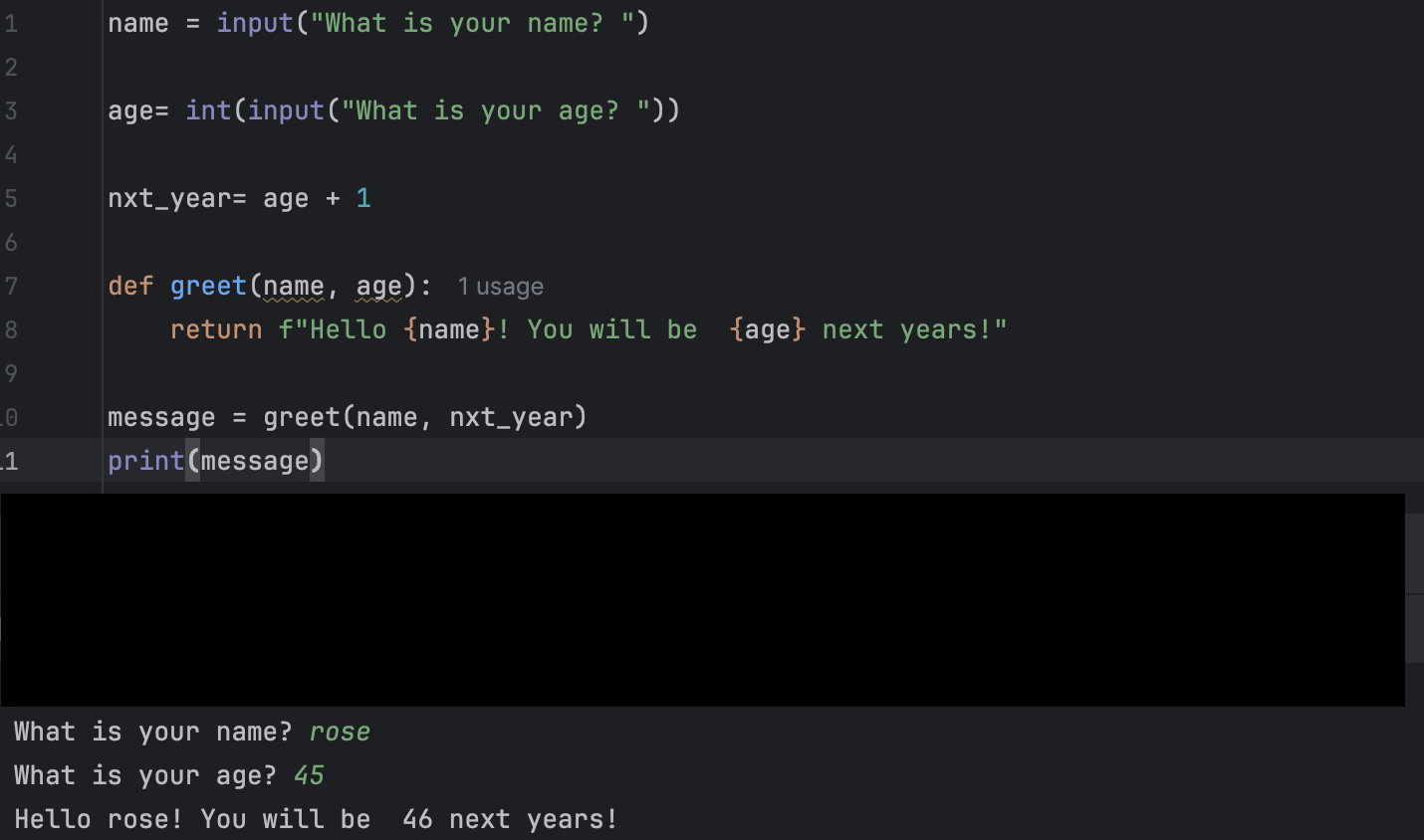
Example Code From Day 4
# Day 4 — Variables, Data Types & User Input
# Asking for input
name = input("What is your name? ")
# Asking for number input and converting it
age = int(input("What is your age? "))
# Doing a calculation
next_year_age = age + 1
# A helper function
def make_greeting(name, age):
return f"Hello {name}, you will be {age} next year!"
# Calling the function
message = make_greeting(name, next_year_age)
print(message)
Expected Output
What is your name? Rekha
What is your age? 32
Hello Rekha, you will be 33 next year!
Output Screenshot
Summary
Today I learned: • How Python stores information using variables • How to work with strings, numbers, and booleans • How to use input() to read user input • How to convert input values into numbers • How to return formatted results from a function
These concepts are the building blocks for writing interactive programs.
What’s Next?
• if / elif / else statements
• Making decisions in Python
• Comparing values
• Running different code based on conditions